|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A Guide To COPD and Asthma
|
|
|
|
|
|
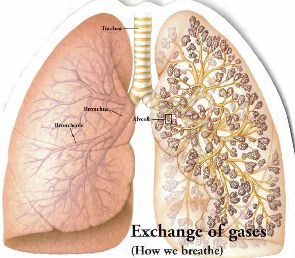
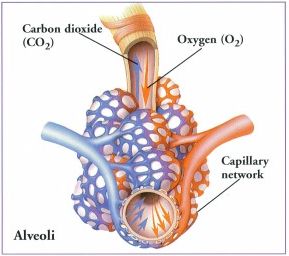
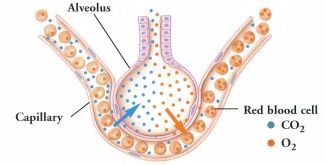
When we breathe, oxygen (O2) travels into our lungs, and is transferred from the alveolus to the red blood cells in the blood stream. |
|
|
|
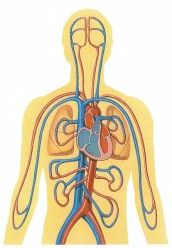
The oxygen (O2)-rich blood circulates throughout the body. This blood circulation transfers the oxygen to all of the major organs of the body as well as supplying oxygen to the muscles we rely on to be mobile. |
|
|
|
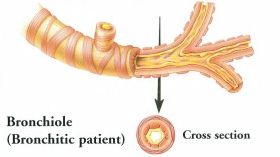
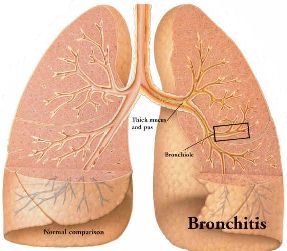
Bronchitis |
 |
|
|
Irritants in cigarette smoke lead to the production of thick mucus and pus, which clog the airway. |
|
|
|
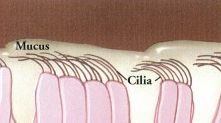
Normal - Enlarged view of bronchial lining. Cilia are the hair like structures responsible for moving inhaled particles out of the lungs. |
|
|
|
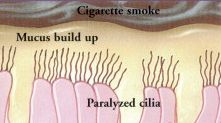
Damaged cilia - Exposure to cigarette smoke for less than a minute paralyzes the cilia. Continued smoking damages cilia so that they are unable to remove mucus and other irritants, which is why a smoker has to regularly cough to move mucus along. |
|
|
|
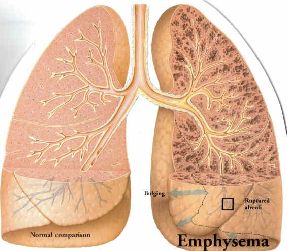
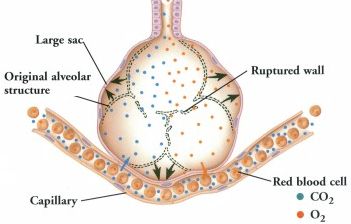
Emphysema |
|
|
|
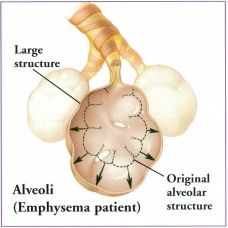
With emphysema, the walls of the individual alveoli rupture leaving large sacs. |
|
|
|
The damaged alveoli cannot efficiently transfer oxygen (O2) to the blood stream, and carbon dioxide (CO2) to the air. |
 |
|
|
Asthma |
|
|
|
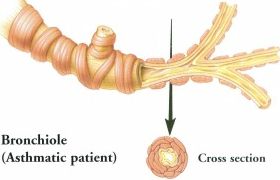
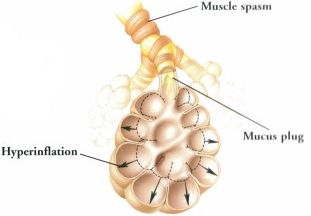
The bronchial tubes are narrowed due to muscle spasm and are often plugged with mucus. |
|
|
|
When bronchioles are blocked, air becomes trapped in the alveoli causing hyperinflation. The result can be a "bulging" lung. |
|
|
|
|
|